AYVAKIT reduced symptom and mast cell burden
in the PIONEER trial1
Primary endpoint at 24 Weeks1
Adding AYVAKIT to BSC demonstrated significantly greater symptom reduction vs placebo + BSC1
ITT analysis: Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation was used to impute the missing values at baseline or Week 24.
Patients treated with AYVAKIT + BSC saw milder symptoms at 24 weeks: 43% (58/134) reported a mild symptom burden (TSS <28) vs only 10% (14/139) at baseline2
LIMITATIONS: Post hoc analysis, data are unranked, not controlled for Type 1 error, and as such results should be interpreted with caution and could represent chance findings. In the PIONEER clinical trial, patients were required to have moderate to severe ISM, defined as an ISM-SAF TSS score ≥28, to participate. For this analysis, mild symptoms were defined as an ISM-SAF TSS <28. Data do not account for degree of change but for those who shifted to a mild symptom burden at Week 24.
ITT analysis: Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation was used to impute the missing values.
LIMITATIONS: Mean change in TSS at all time points except Week 24 were prespecified, nonranked endpoints and were not adjusted for multiplicity. Therefore, treatment differences at these time points cannot be regarded as statistically significant and results should be interpreted with caution.
BSC=best supportive care; ISM=indolent systemic mastocytosis; ISM-SAF=Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis-Symptom Assessment Form; ITT=intention to treat; TSS=total symptom score.
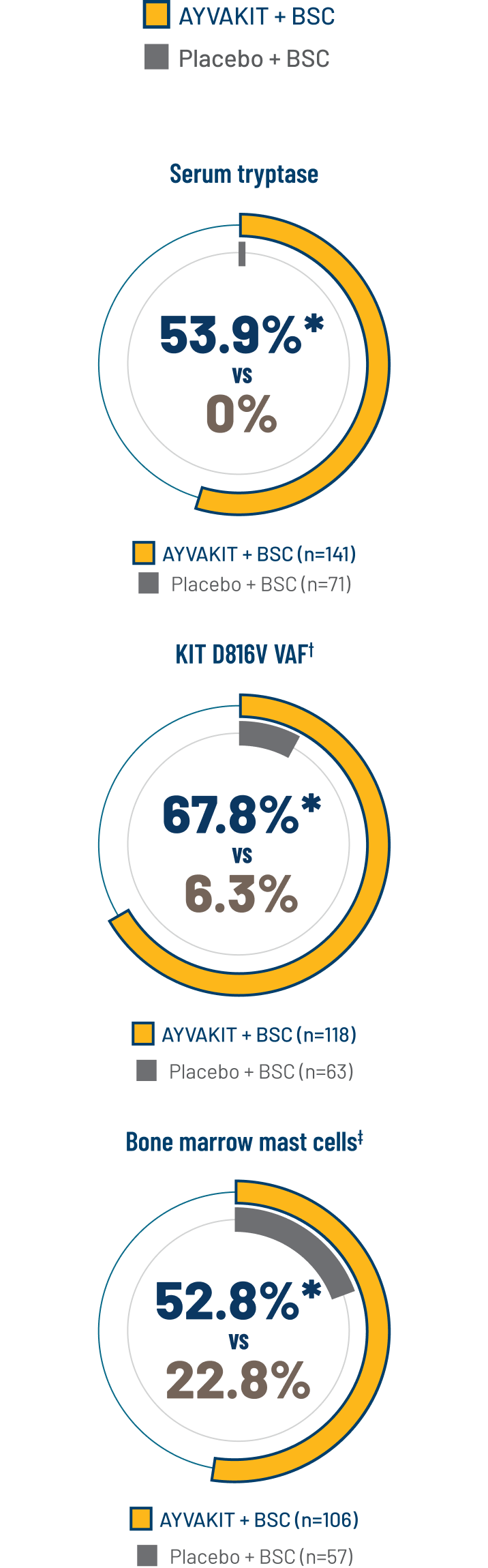
Significantly more patients treated with AYVAKIT had reductions in objective measures of mast cell burden1
KEY SECONDARY ENDPOINTS AT 24 WEEKS1
PROPORTION OF PATIENTS ACHIEVING ≥50% REDUCTION IN OBJECTIVE MEASURES OF MAST CELL BURDEN AT 24 WEEKS1
ITT analysis: For patients with high-dose steroid use within 7 days before Week 24, or greater than 14 consecutive days at any point from baseline to Week 24, the Week 24 score was set to missing.
*2-sided P<0.0001.
†Percent of patients with ≥50% reduction in peripheral blood KIT D816V VAF or undetectable.
‡Percent of patients with ≥50% reduction in bone marrow mast cells or no aggregates.
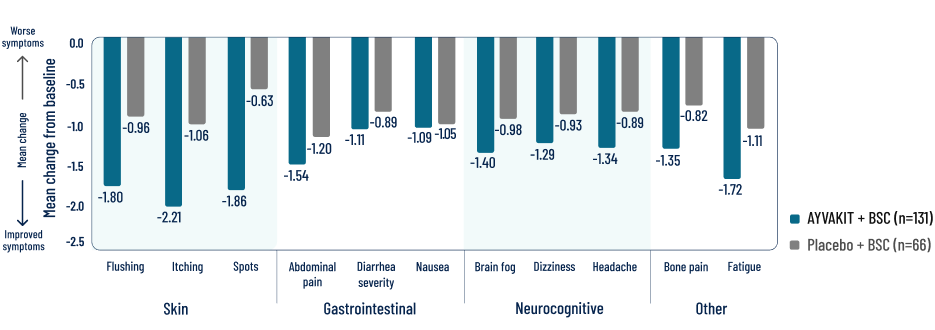
Individual symptom scores and skin outcomes at 24 weeks
EXPLORATORY endpoint
Decreases in symptom severity were observed across all domains, including skin, gastrointestinal, and neurocognitive4
ITT analysis: In this analysis, if a patient was missing more than 7 days of the score between baseline score and Week 2 score, it was considered as missing for the patient. If a patient missed more than 7 days of the score from the 14-day period for calculating the Week 24 score, then the Week 24 score was considered as missing.
LIMITATIONS: Individual components in a descriptive exploratory analysis were prespecified, nonranked endpoints, not adjusted for multiplicity, and not powered. Therefore, data should be interpreted with caution, conclusions cannot be drawn, and treatment differences cannot be regarded as statistically significant.
Reductions were observed in patients’ most severe symptom, defined as the symptom with the highest score at baseline3
BSC=best supportive care; KIT=KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; ISM-SAF=Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis-Symptom Assessment Form; TSS=total symptom score; VAF=variant allele fraction.
Explore the safety profile of AYVAKIT
SAFETY
References: 1. AYVAKIT [prescribing information]. Cambridge, MA: Blueprint Medicines Corporation; November 2024. 2. Data on file. Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Cambridge, MA. 2024. 3. Gotlib J et al. NEJM Evidence. 2023;2(6). Published online May 23, 2023. doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2200339 4. Data on file. Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Cambridge, MA. 2023. 5. Maurer M et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023;151(2) (suppl):AB340.